Suviksha Hirawat
Posts tagged with User Research
Showing 11 - 20 of 36 items

This blog post reflects on the learning experience I had as a novice user research (UX) intern at the U-M Library. Through this nurturing and eye-opening experience, I enhanced my understanding of research operation, the activities which support the user research conducted by library employees in the Design & Discovery unit of the library.
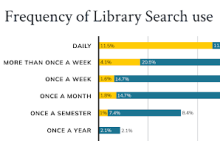
The U-M Library UX + Design Team conducted a benchmark survey in late 2022 aiming to understand people’s experience with Library Search. Objectives included measuring user satisfaction, identifying audience needs, and comparing results with Harvard University’s survey using the same methodology. Survey findings guided the development of the Library Search Product Statement as well as user centered improvements such as implementing LibKey Direct-to-PDF API, and refining catalog results filters.

For the past year, U-M Library Digital Collections have been undergoing some big design changes. This blog post tells the story of launching and evaluating the usability of collections containing a new type of media: audio and moving images (AMI). In a research study consisting of a heuristic evaluation and 50 usability tests with a diverse group of users, the team uncovered over 20 mostly minor usability issues, recommended improvements to the interface that will be implemented in 2024 and beyond, and learned a lot about the complexity of library products along the way.
User research is best performed as an iterative process, where each round of testing provides valuable insights to lead to the next stage of development. The recent uplift on the University of Michigan Library’s Image Digital Collections offers a prime example of iterative user research, as it included testing phases for early mockups, plug-in image viewers, and an interactive coded version of the site. By continuously testing, we were able to identify potential issues early and to refine the site to better meet user needs.

In Fall 2022, the Library Environments department began a pilot of two designated “zoned” spaces in response to user feedback asking for more information about what to expect from a study space. We conducted focus groups and integrated participatory design to learn about how users are perceiving and experiencing these labeled spaces.
As students, we all know the struggle of trying to find the perfect study space on campus. The Library Environments UX Research Team and the Library Information Technology Design and Discovery (D&D) Team worked together to improve the user experience of the Library’s study spaces booking website.
The University of Michigan Library is home to a vast collection of materials representing dozens of languages. U-M Library Catalog Search, however, can cause difficulties for users searching for materials in languages other than English. In Summer 2021 we conducted an exploratory study on the experience of searching for non-English materials within U-M Library Catalog Search in order to better understand challenges users face, how they overcome them, and what we can do to mitigate the problem.

U-M Library’s universal header is the light gray bar at the top of the library website and Library Search that aims to help people recognize that they’re on a U-M Library website, and links to our different sites and services through the “Explore” menu. In the fall of 2020, the Design System Team conducted remote usability testing that helped us to understand people’s experiences and identify opportunities for improvement.

U-M Library’s Library Search launched in 2018 as a unified search engine application containing five previously distinct interfaces: Catalog, Articles, Databases, Online Journals, and Library Websites. Library Search was a big change for users, and an increase in user support requests suggested that further exploration was needed to pinpoint user pain points. The authors began an exploratory study that helped understand users’ experiences and identified areas for continued work.

In three blog posts, the authors describe a multi-year library service design project. This last post describes the team’s prototyping and testing processes, and our resulting interactive exercise.