Pablo Alvarez
Posts by Pablo Alvarez
![Detail from copperplate describing the bookbinding workshop, from Encyclopédie, ou Dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers, par une société de gens de lettres. 17 vols. 11 vols of plates. (Paris: Briasson [etc.] Genève, C. J. Panckoucke, G. Cramer et S. de Tournes, 1762-1776)](/sites/default/files/styles/medium/public/plate_25_21_1.jpg?itok=ZBt0QAwg)
We are very pleased to invite you all to the first session of a series of virtual encounters on various aspects of book history. Our first online meeting is devoted to bookbinding and is scheduled for July 6, 11:00 am (EDT). This session, and the series, are organized by Pablo Alvarez (UM) and Benito Rial Costas (UCM), and will be hosted by the University of Michigan Library and the Facultad de Ciencias de la Documentación of the Universidad Complutense de Madrid on Zoom. The session is free of charge and open to all, but registration is required.

We are pleased to announce the opening of a new online exhibit: Written Culture of Christian Egypt: Coptic Manuscripts from the University of Michigan Collection. This online display is a virtual record of an actual physical exhibit that took place at the Audubon Room of the University of Michigan Library between November 12, 2018 and February 17, 2019. Curated by Alin Suciu and Frank Feder (Göttingen Academy of Sciences and Humanities, Germany), and with the collaboration of Pablo Alvarez (Special Collections Research Center), the display includes highlights from our collections of Coptic fragments and codices held at the Papyrology Collection and the Special Collections Research Center.

We are very pleased to announce the recent acquisition of the first comprehensive treatise ever published about the illustration technique of woodcut: Jean Michel Papillon. Traité historique et pratique de la Gravure en bois. 2 vols. (Pierre Guillaume Simon, 1766). Papillon’s manual is particularly remarkable for including a fully illustrated step-by-step depiction of the sixteenth-century technique of chiaroscuro.

When examining a selection of rare books that had been requested for a class presentation about the impact of censorship in early modern Spain, I noticed something truly remarkable in one of these books. Our copy of the eighteenth-century edition of Francisco de Quevedo y Villegas’ El Parnaso español y musas castellanas, published in Barcelona in 1703, had been manually, and massively, expurgated by a representative of the Spanish Inquisition, Joseph Pinell, as he himself stated on the title page: Expurgavi ex Commisione S(anc)ti Officii die 8 Aprilii/ Joseph Pinell, Supr(emus). Missionum (I, Joseph Pinell, the highest of delegates, have expurgated it by a mandate of the Holy Inquisition on April 8 1760).

We are pleased to report about our recent acquisition of the first edition of Alessandro Vellutello’s influential commentary on Dante Alighieri’s Divine Comedy, which was published by Francesco Marcolini da Forlì in Venice in 1544. Undeniably, this edition marked a significant shift in the history of the iconography and reception of Dante’s poem, departing from the previous allegorical interpretations by Cristoforo Landino and Girolamo Benivieni, and challenging Antonio Manetti’s reconstruction of the topography of Hell as described by Dante.

This blog post features an extraordinary well-preserved copy of what is perhaps one of the earliest extant drawing manuals that were published in Western Europe in the first half of the seventeenth century. Its author is Odoardo Fialetti, an Italian artist whose professional life flourished in Venice at the end of the sixteenth century; Fialetti had access to Tintoretto’s workshop, eventually becoming an accomplished copperplate engraver. While more than 200 engravings are attributed to him, Fialetti is best known for the illustrations he created for his two drawing manuals published in Venice in 1608 and 1609. Indeed, these two manuals became extremely popular among young artists, having a considerable impact on subsequent European manuals of this type published throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. In a few words, a drawing manual consisted of a collection of images of the human body that served as models for young apprentices; these illustrations represented the body in full or in sections, and were arranged in increasing difficulty. Essentially, these manuals were self-taught guides and, since they were meant to be heavily used as opposed to be shelved merely for reference, currently they are rarely found at libraries, museums, or private collections.
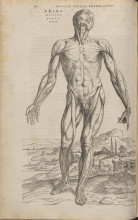
Join us today for our December Special Collections After Hours open house! You are all invited to explore a great variety of early printed books containing illustrations of the human body that reflect the science of dissection as well as the latest artistic theories in early modern Europe. The display will include richly illustrated treatises by well-known authors such as Leonardo da Vinci and Andreas Vesalius. Refreshments.
Time: 4:00-6:00 pm.
Location: Special Collections Research Center. Hatcher Library Room 660D
Time: 4:00-6:00 pm.
Location: Special Collections Research Center. Hatcher Library Room 660D

I recently came across this sixteenth-century introductory manual designed to teach Christian biblical scholars how to read and understand works in Hebrew and other Oriental languages without punctuation and stress marks. But what makes our copy remarkable is that the names of well-known Protestant scholars, and other infidels, have been carefully crossed out, that is, expurgated, following the Inquisition's recommendations to censor authors considered heretical according to the teachings of the Church of Rome.

When searching for manuscripts of Hrabanus Maurus' medieval encyclopedia De rerum naturis (On the Natures of Things) in the database Digital Scriptorium, I came across a leaf fragment held at Columbia University Libraries (Plimpton MS 128 ) which, in terms of its handwriting and style of illumination, was clearly connected to a leaf fragment held at the University of Michigan Library (Mich. Ms. f. 14).

According to Giorgio Vasari’s biographies, The Lives of the Most Excellent Italian Architects, Painters, and Sculptors, Leonardo da Vinci died on May 2, 1519. As museums around the world are commemorating the 500th anniversary of the death of Leonardo with various exhibits, we would like to join the celebrations of Leonardo’s legacy by highlighting our copies of some early printed editions of his Trattato della Pittura (Treatise on Painting).